Mobile Robot Navigation in Dynamic Environments
Abstract
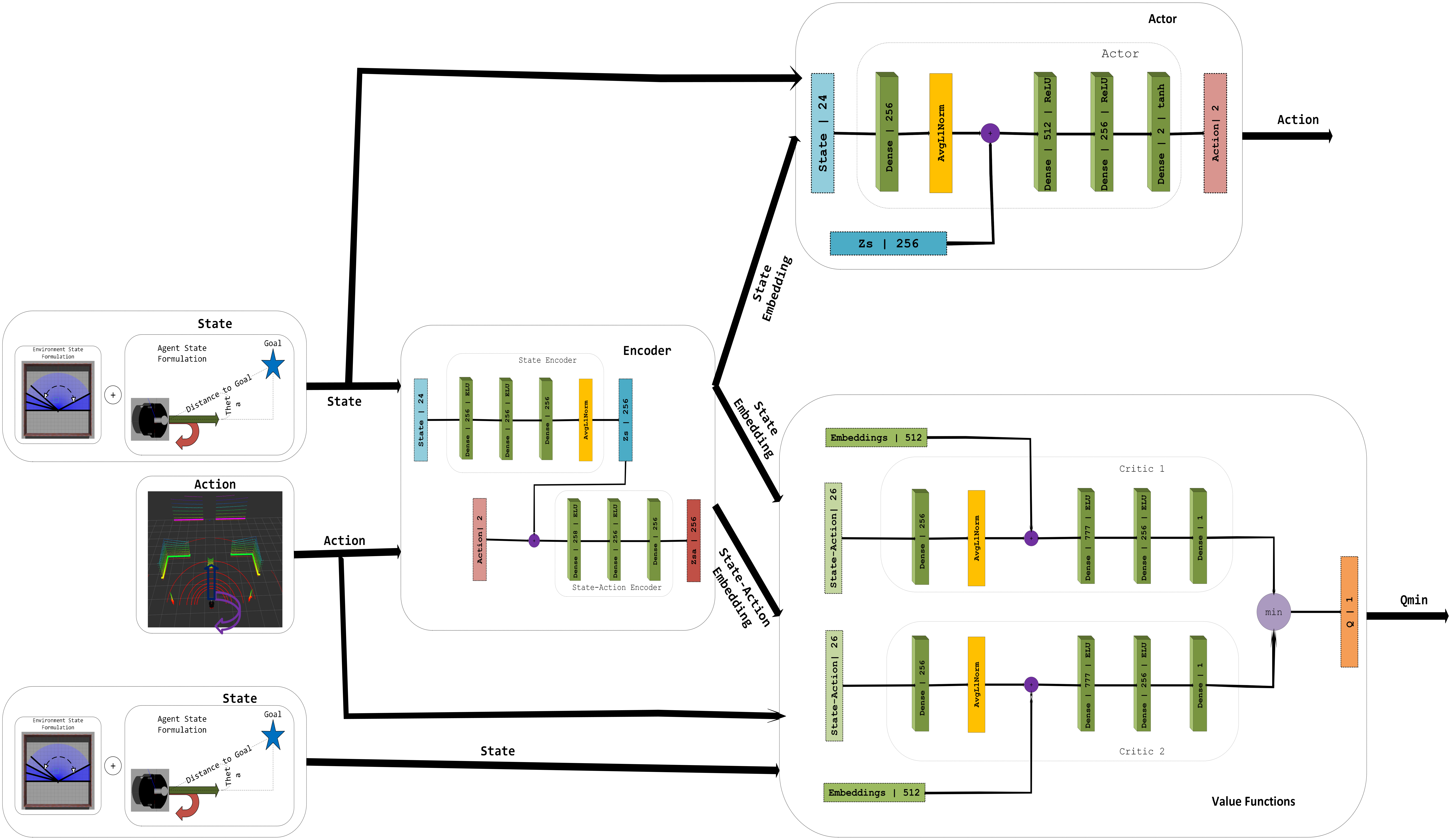
This paper presents a framework for mobile robot navigation in dynamic environments using deep reinforcement learning (DRL) and the Robot Operating System (ROS). The framework enables proactive adaptation to environmental changes. Traditional navigation methods typically assume a static environment and treat moving obstacles as outliers during mapping and localization. This assumption severely limits the robustness of these methods in highly dynamic settings such as homes, hospitals, and other public spaces. To overcome this limitation, we employ encoder networks that jointly learns state and state–action representations by minimizing the mean squared error (MSE) between predicted and actual next-state embeddings. This approach explicitly captures the environment’s transition dynamics, enabling the robot to anticipate and effectively navigate around moving obstacles.
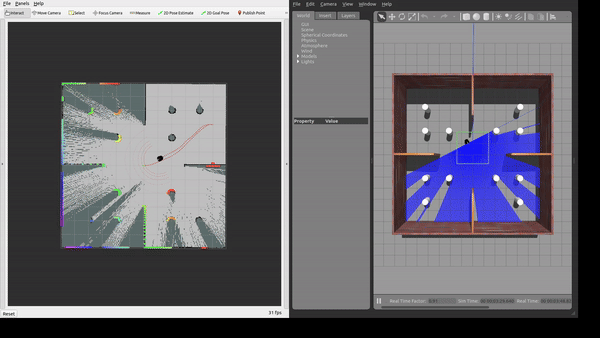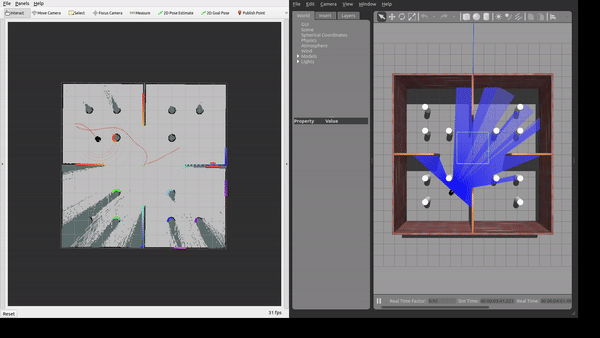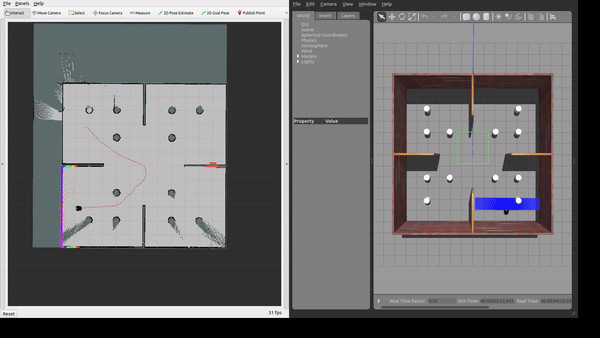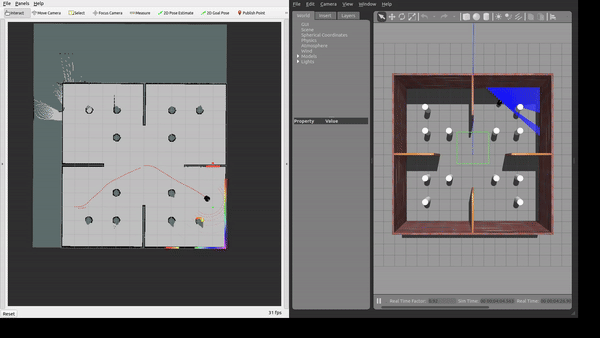
We evaluate the proposed framework through extensive simulations in custom Gazebo worlds of increasing complexity,ranging from open spaces to scenarios with densely populated static obstacles and moving actors. We assess performance in terms of success rate, time to goal, path efficiency, and collision rate. Results demonstrate that our approach consistently improves navigation performance, particularly in highly dynamic environments.
Network Architecture
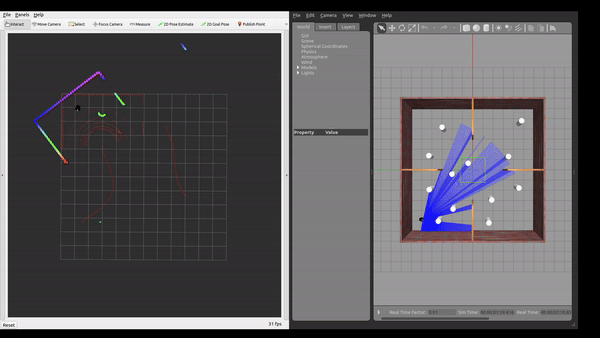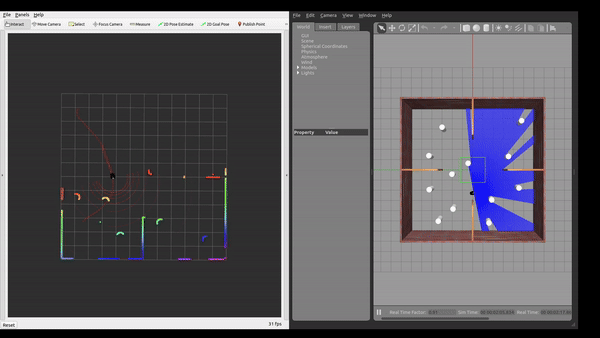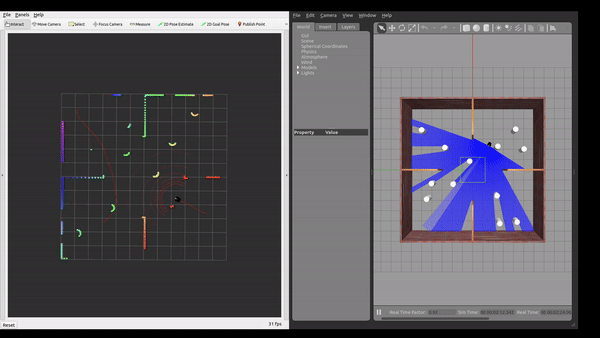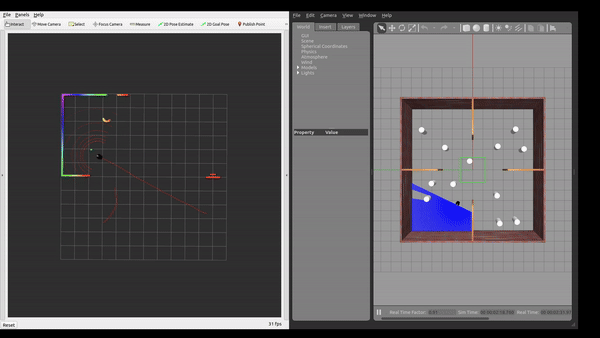
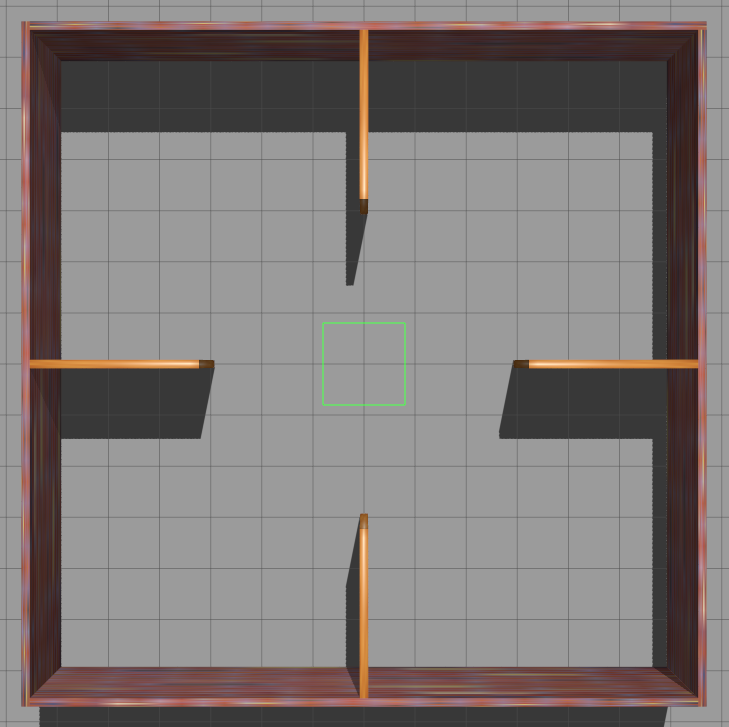
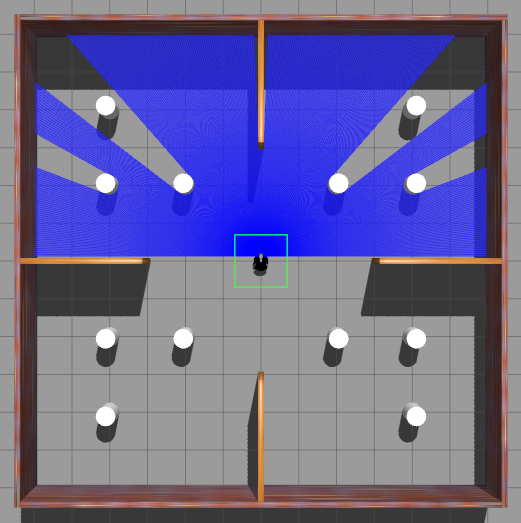
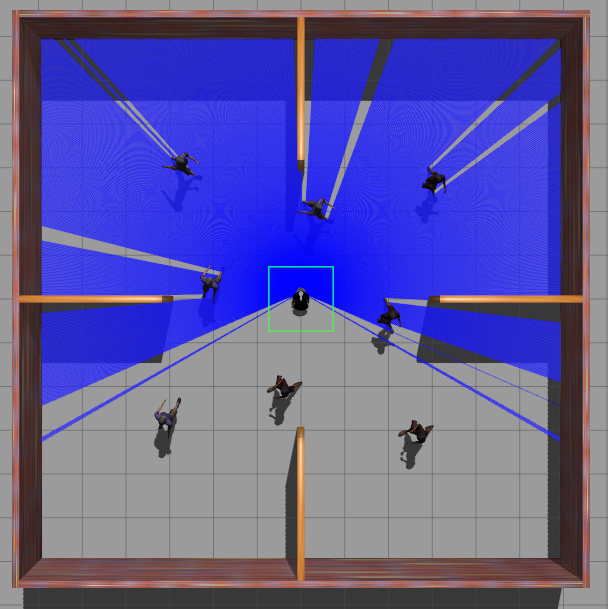
Simulation Environment
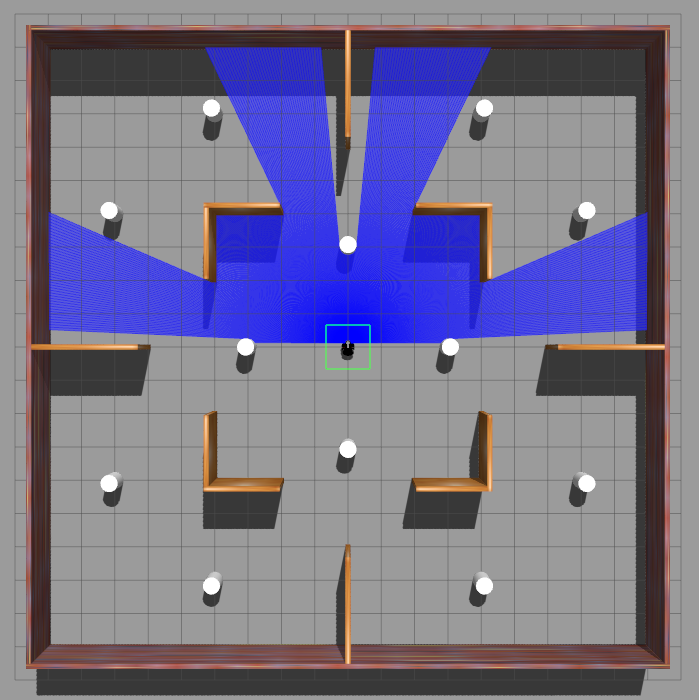
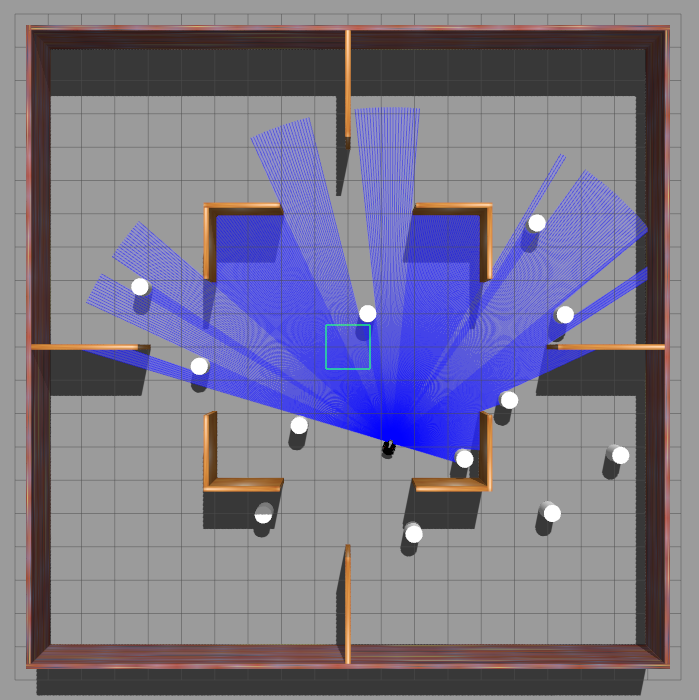
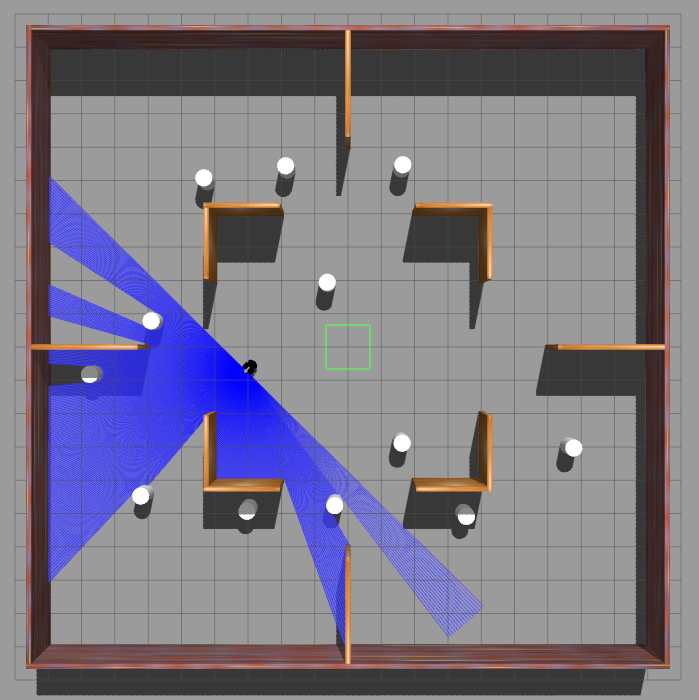
The framework was tested in Gazebo simulation environments with increasing level of complexity.
@INPROCEEDINGS{nurye2025,
author={Nurye, Ahmed Yesuf and Jarzebowska, Elzbieta},
booktitle={2025 29th International Conference on Methods and Models in Automation and Robotics (MMAR)},
title={Deep Reinforcement Learning for Mobile Robot Navigation in Dynamic Environments},
year={2025}
}